Nutritional Orthopedics and Space Nutrition as Two Sides of the Same Coin

From Surgery Recovery to Space Missions: How Nutrition Supports Muscle and Bone Health
Since the Moon landing, nutritional research has focused on keeping humans healthy in space.
When astronauts are in zero-gravity environments for an extended amount of time, they experience muscle loss.
Muscle loss that is very similar to recovery after surgery in the medical field of orthopedics.
Orthopaedics is a branch of medicine that focuses on the bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. It deals with injuries, diseases, and conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system, such as broken bones, arthritis, and back problems.
Nutritional Orthopedics and Space Nutrition are alike, because they address similar challenges despite focusing on different environments. Both deal with the effects of extreme conditions on the human body, especially the musculoskeletal system.
Key Overlaps Include
-
Muscle and Bone Health
Both aim to prevent muscle loss and bone weakening, which occur in surgical patients and astronauts alike.
-
Nutritional Solutions
They focus on tailored diets with essential nutrients like vitamin D, calcium, and protein to promote healing and strength.
-
Metabolic Stress
Both fields study how stress affects metabolism and use nutrition to counteract negative effects.
-
Isolation and Recovery
Orthopedic patients and astronauts both face isolation and unique recovery challenges that require innovative nutritional approaches.
Zero Gravity and Surgery Recovery: The Shared Science of Nutrition for Strength
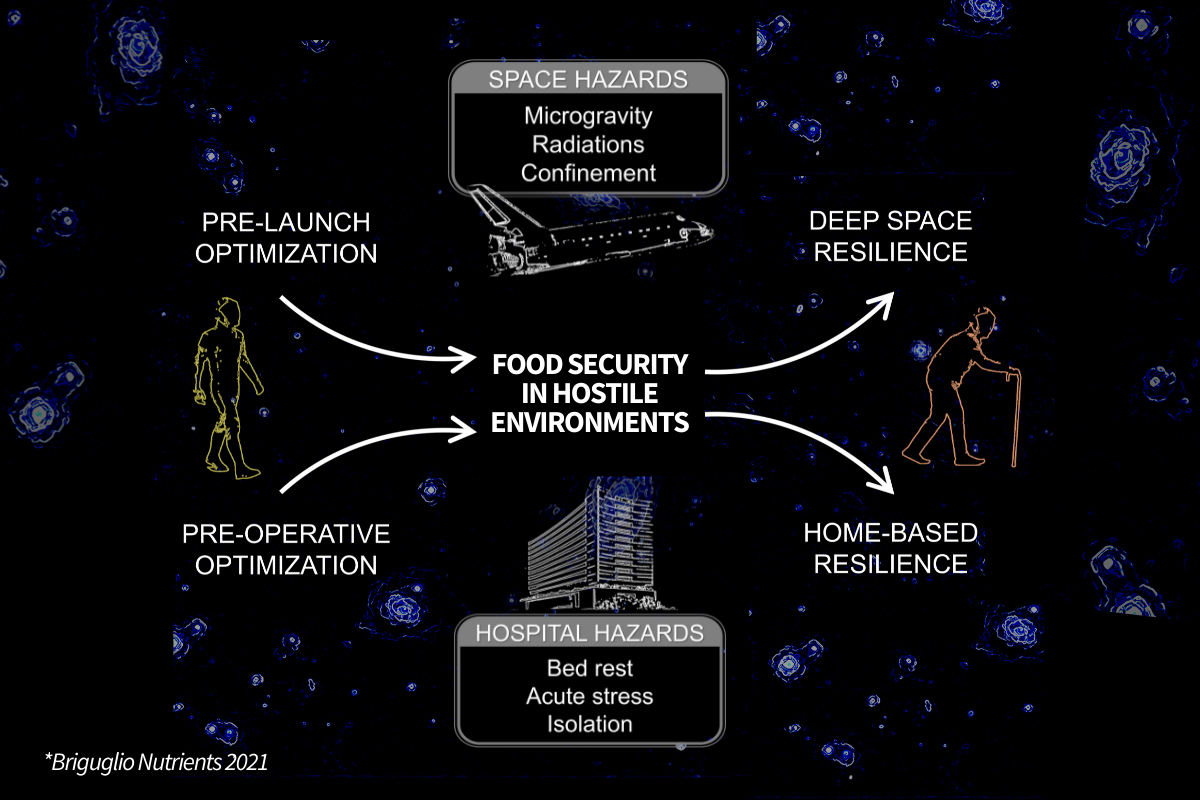
Microgravity
Astronauts exposed to microgravity experience:
1 month
- 20% decrease skeletal muscle mass.
- 30% decrease skeletal muscle strength.
6 months-1 year
- 8-10 years of MSK degeneration
The preservation of muscle mass and reduction of strength loss during bedrest and spaceflight have been demonstrated in multiple studies through the use of essential amino acid supplementation.
-

NASA studies aimed to preserve muscle mass have demonstrated Targeted Nutritional Supplementation to preserve muscle loss even in extreme conditions such as 28 of days of bed rest.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004(4)
-

Targeted nutritional supplementation can improve muscle gain in the most challenging patients.
HIV patients who were supplemented with ARG/GLUT/HMB for 8wks had a significant increase in LBM in comparison to placebo.
Clark JPEN May-Jun 2000 (5)
Skeletal Muscle Mass
Dynamic balance between:
Muscle Protein Synthesis (MPS)
+/-
Muscle Protein Breakdown (MPB)
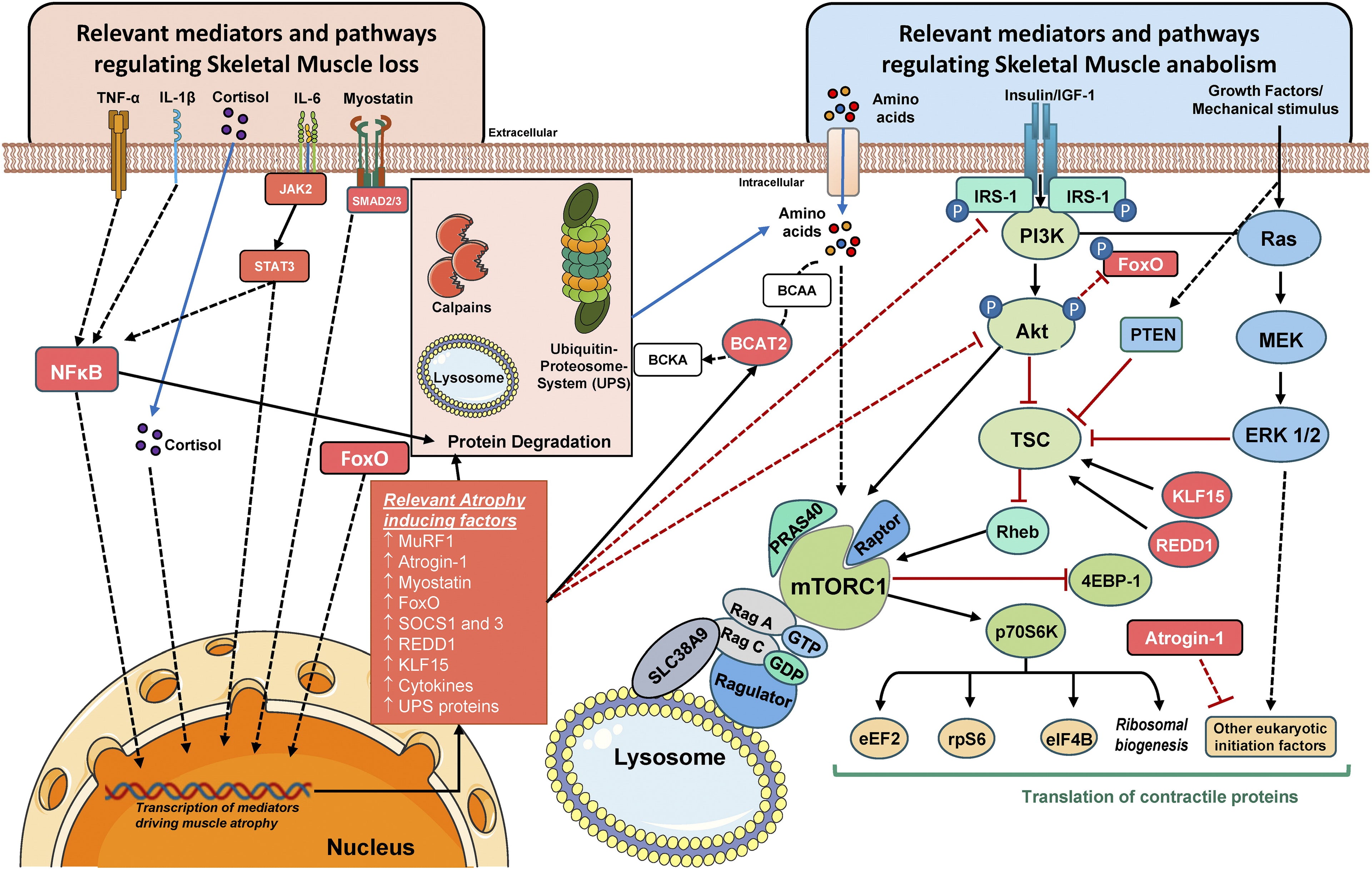
The balance between muscle protein breakdown (MPB) and muscle protein synthesis (MPS) largely determines skeletal muscle mass, with both processes occurring continuously and simultaneously.
Proteins in muscle tissue undergo constant remodeling through the actions of MPB, which utilizes various proteolytic systems to break down proteins and release amino acids and peptides into the muscle's intracellular pool. However, in healthy individuals, MPS usually offsets MPB, especially after protein meal ingestion, causing hyperaminoacidemia and mechanical loading stress on the skeletal muscle.

The XR® Perioperative Optimization Program is Like Recovery Powered by NASA’s Research
Whether you're in space or recovering from surgery, supporting amino acid supplementation, mechanical loading prehabilitation, and a high-protein diet is vital.
As you may recall, both directly address the challenges of maintaining and rebuilding muscle, bone, and overall physical function in 3 different ways.
-
Amino Acid Supplementation
Promotes Muscle Repair: Amino acids, especially essential ones like leucine, are the building blocks of protein and are critical for repairing muscle tissue after surgery.
Prevents Muscle Loss: Surgery and recovery periods often involve inactivity, leading to muscle atrophy. Supplementing with amino acids helps mitigate this loss.
Boosts Healing: Amino acids support collagen synthesis, which aids in tissue repair and wound healing. -
Mechanical Loading Rehabilitation
Builds Strength Before Surgery: Prehabilitation (strengthening exercises before surgery) conditions muscles and bones, making the body more resilient during the recovery phase.
Preserves Muscle Mass: Mechanical loading (like resistance exercises) prevents rapid muscle loss from inactivity during recovery.
Enhances Circulation: Exercise improves blood flow, which helps deliver nutrients and oxygen to tissues, supporting faster healing. -
High-Protein Diet
Provides Essential Nutrients: Protein is necessary for muscle repair, immune function, and overall tissue recovery.
Preserves Lean Mass: High-protein intake helps minimize the loss of muscle mass during periods of reduced activity.
Supports Bone Healing: Protein works alongside nutrients like calcium and vitamin D to strengthen bones after surgical interventions.
Together, these strategies create a comprehensive approach to recovery. So if you’re looking to preserve muscle, maintaining strength, and accelerate healing the XR® formulation is right for you.
Collapsible content
References
(ref #1) Kortebein P, Symons TB, Ferrando A, et al., J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2008;63(10):1076‐1081.
(ref #2) Kortebein P, Ferrando A, Lombeida J, et al: Effect of 10 days of bed rest on skeletal muscle in healthy older adults. JAMA 2007;297:1772-1774.
(ref #3) Paddon-Jones D, Sheffield-Moore M, Cree MG, et al: Atrophy and impaired muscle protein synthesis during prolonged inactivity and stress. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91:4836-4841
(ref #4) Paddon-Jones D, Sheffield-Moore M, Urban RJ, et al: Essential amino acid and carbohydrate supplementation ameliorates muscle protein loss in humans during 28 days bedrest. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89:4351-4358
(ref #5) Robert. H. Clark MD, J Parenter Enteral Nutr May-Jun 2000;24(3):133-9.Nutritional Treatment for Acquired Immunodeficiency Virus-Associated Wasting Using β-Hydroxy β-Methylbutyrate, Glutamine, and Arginine: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
(ref #6) Gao R, Chilibeck PD. Nutritional interventions during bed rest and spaceflight: prevention of muscle mass and strength loss, bone resorption, glucose intolerance, and cardiovascular problems.Nutr Res. 2020;82:11-24. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2020.07.001
(ref #7) Briguglio, M. Nutritional Orthopedics and Space Nutrition as Two Sides of the Same Coin: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020483
Recovery collection
-
XR® Surgical Recovery Program
Regular price From $399.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
XR® Recovery Bundle
Regular price $254.49 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
XR® Recovery Supplement
Regular price From $129.99 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
XR® Pre-Op Carb Loading | 3-pack
Regular price $21.40 USDRegular priceUnit price / per